
Power analyzer is connected but there is no communication.
Cause of failure: instrument settings.
Solution: check whether the address and baud rate of the instrument are corresponding to the system software, and ensure that all the instruments connected to the same communication channel have no overlapping addresses and the baud rate is consistent.
Power analyzer has no display.
Cause of failure: check whether the power supply voltage input is normal.
Solution: check whether there is virtual connection in the power supply line. Use a multimeter to measure whether the voltage of the instrument power supply terminal (L+, N-) is normal and meets the order requirements. Distinguish between positive and negative terminals for DC power supply, and pay attention to whether the output power supply meets the requirements.
What is derating?
We recommend that the actual working current of a fuse should not exceed its rated current under the ambient temperature of 20℃. While selecting the fuse, environment and working conditions should be considered, such as the sealed situation, air flow, wire sizes(length and section) and instantaneous peak value, etc.. The current load capability of a fuse is tested under the ambient temperature of 20℃. However the actual load capability is affected by the ambient temperature. The higher the ambient temperature, the higher the working temperature and the shorter the service life of a fuse will be. Conversely, the service life of a fuse will be longer when working under a lower ambient temperature.
The following typical curve displays the effect of ambient temperature on the current load capability.
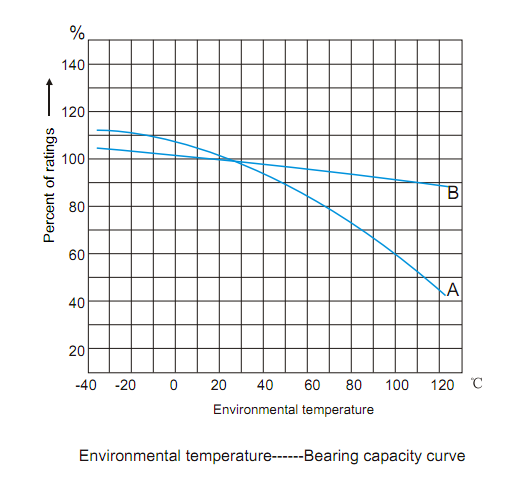
Note: A: (gG) type for line protection
B: (aR) type for semiconductor protection
Example: Assume that the ambient temperature is 20℃, choose a gG type fuse with rated current In=63A, reducing working current is necessary when the ambient temperature is changed to 70℃. In the environmental temperature-bearing capacity curve, A shows that the rating should be 78% at 70℃, and the new rating should be determined as: In= 6 3/0.78 =80.77A
So a fuse with rated current In=80A should be selected for the new ambient temperature.
Selecting overcurrent protection.
During normal load conditions, the fuse must carry the normal operating current of the circuit without nuisance openings. However, when an overcurrent occurs, the fuse must interrupt the overcurrent and withstand the voltage across the fuse after internal arcing. To properly select a fuse, the following items must be considered:
• Voltage rating (AC or DC voltage)
• Current rating
• Normal operating current
• Ambient temperature
• Overload conditions and opening times
• Available short circuit current
• Melting Integral (I²t)
• Pulse and In-rush characteristics
• Characteristics of equipment or components to be protected
• Physical size and available board space
• Standards requirements
How to calculate a relay for a three phase motor load? example:
U:400V
P:15KW
Efficiency: 0.8 for a motor < 5KW
Efficiency: 0.9 for a motor > 5KW
Power factor: 0.8 for a motor < 5KW
Power factor: 0.9 for a motor > 5KW
V3 = 1.732
Nominal current absorbed by the motor:
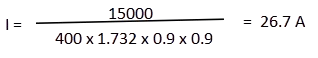
The current rating of the relay must be 4 * I of the motor in order to withstand starting currents: >>> 106.8 A >>> it’s necessary to take a 125 A relay.
Advantages of Solid State Relays in comparison to a electromechanical relays ?
Because of their semiconductor technology-based design, SSRs provide a higher degree of reliability, longer life and reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI), as well as faster response times and vibration and shock resistance, when compared to the EMR counterparts. This is due to the fact that SSRs have no mechanical contacts to wear out or arc, which is the primary cause for EMR failure.
What does “zero-voltage turn-on” mean? (or synchronous or zero-cross)
The relay will only turn on when the mains (output) voltage is near zero.
What does instantaneous or random turn-on mean?
When the control voltage is on the relay will switch on at the same moment, whatever the mains voltage value.
In what application would I use a zero voltage turn-on V. a random turn-on relay?
Zero-cross relays are used with resistive loads while random turn-on relays are used with inductive loads (motors, transformers, coils etc.).